- I am also posting Lauren's solutions for Assignment 2.
- I am posting Brock's solutions for Assignment 2.
- This is what I wrote during the final exam.
- This is what I wrote during the exam.
- Here is an animation which might help you solve Problem 3 (at least the first part of it) on Assignment 2.
Place the cursor over the image to start the animation.
|
|
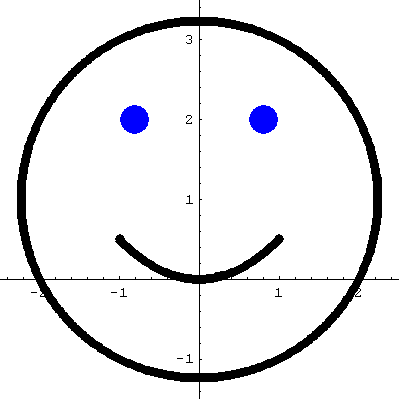
- Below is an animation based on which we can answer the question: "How long is a smile?"
Place the cursor over the image to start the animation.

|
|
- Please add the problems 31 and 32 in Section 8.2 to the list of suggested homework problems.
-
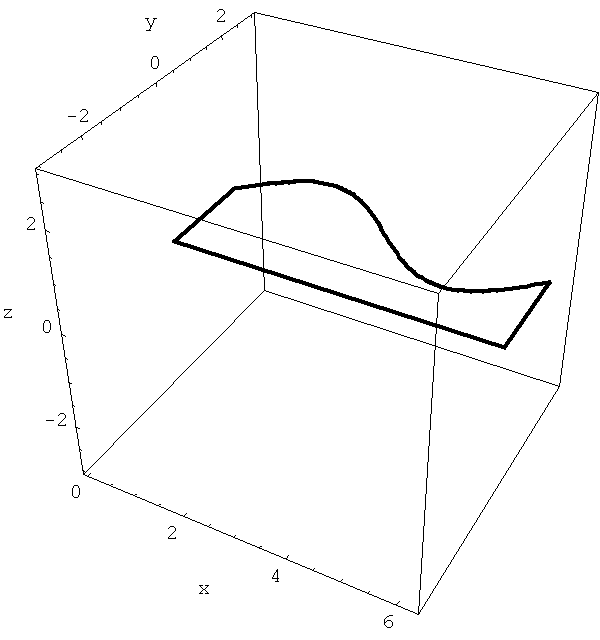
Here is one more animated example of a solid of revolution. Isn't this a nice vase? If you ever get a chance to design a vase please use the following function as a guide: y=2+sin x where x is in the interval [0,2 pi]. Then it will be a nice exercise to calculate exactly the volume of that vase.
Place the cursor over the image to start the animation.
-
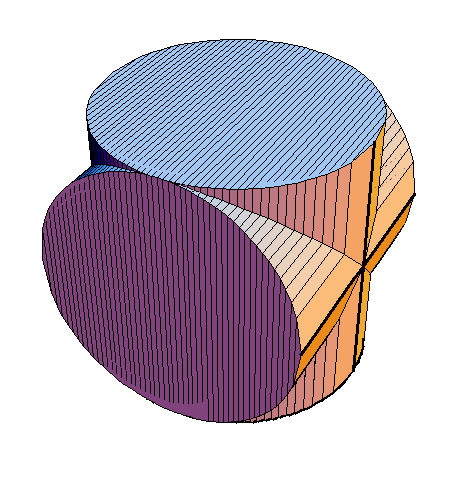
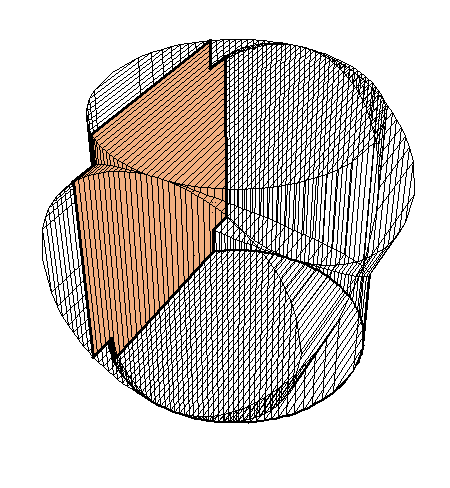
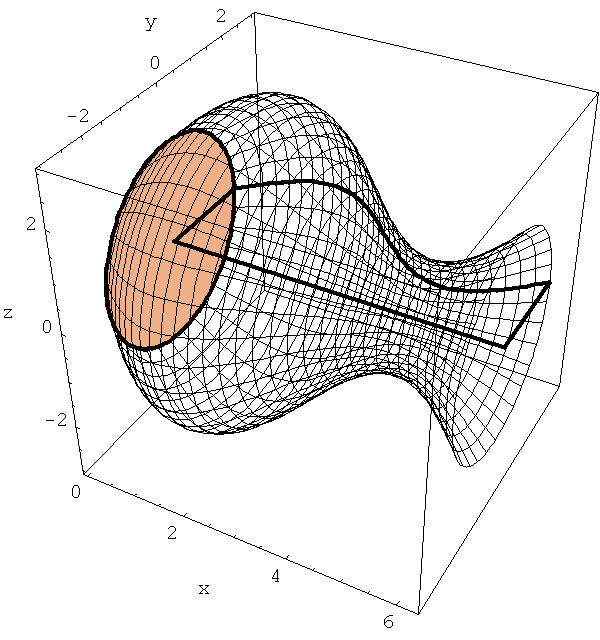
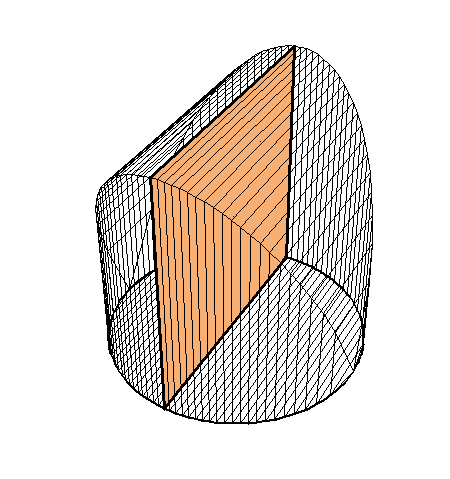
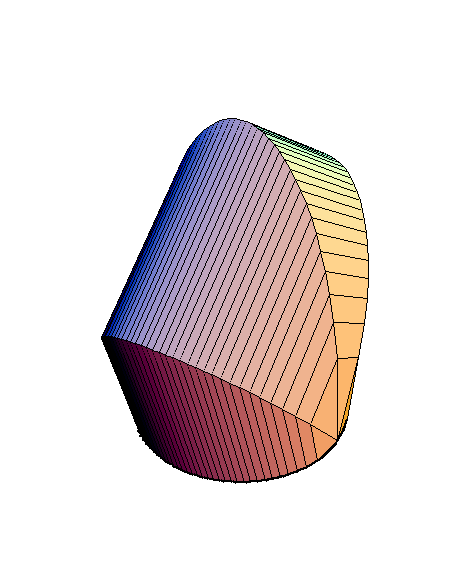
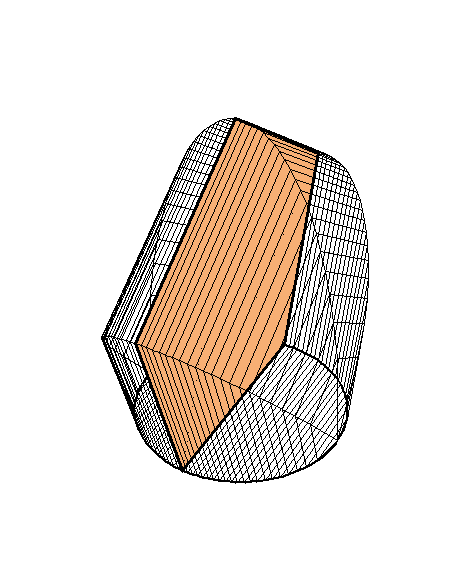
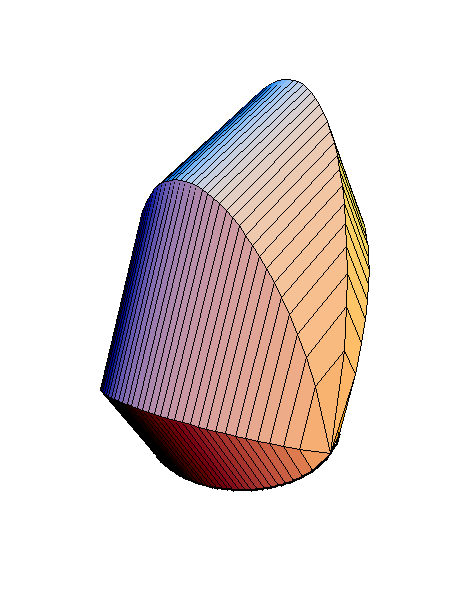
The following family of six examples is inspired by the subsection "Volumes of Regions of Known Cross-Section" of Section 8.2. Here the base is always a unit disk and the cross-sections are
regular polygons: equilateral triangle, square, regular pentagon, regular hexagon, regular heptagon and regular octagon. There are twelve animations below. They follow the pattern of earlier animations.
Place the cursor over the image to start the animation.
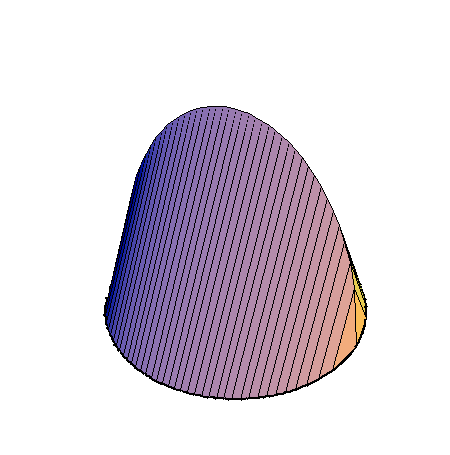
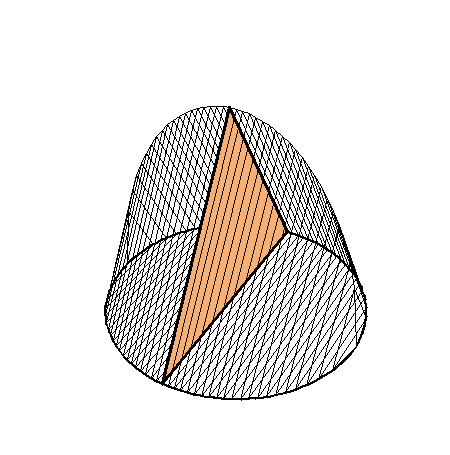
A cross-section is an equilateral triangle.
Place the cursor over the image to start the animation.
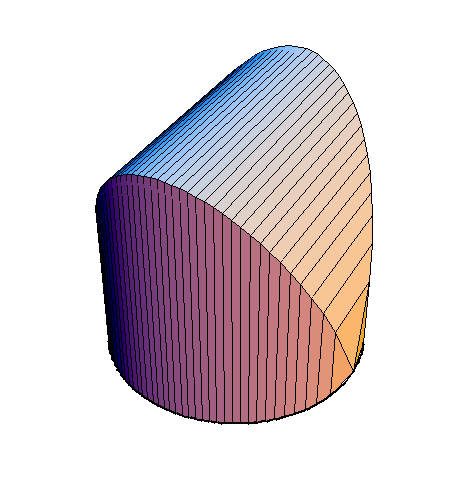
A cross-section is a square.
Place the cursor over the image to start the animation.
A cross-section is a regular pentagon.
Place the cursor over the image to start the animation.
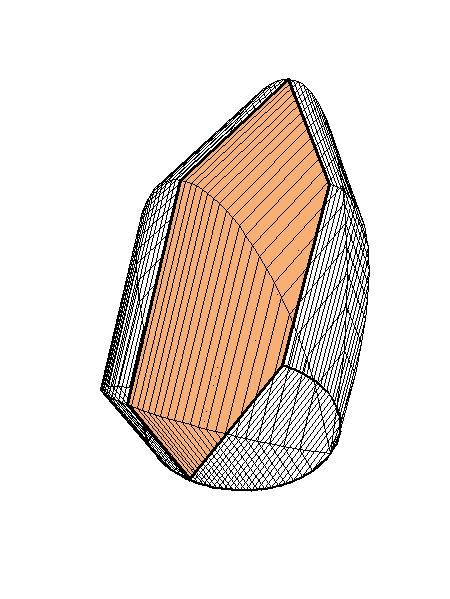
A cross-section is a regular hexagon.
Place the cursor over the image to start the animation.
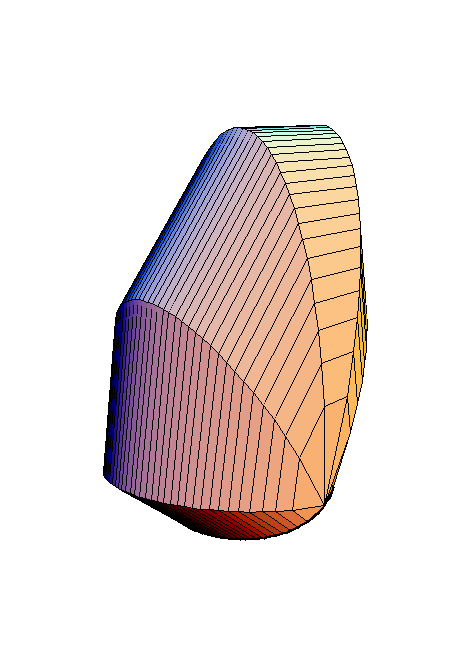
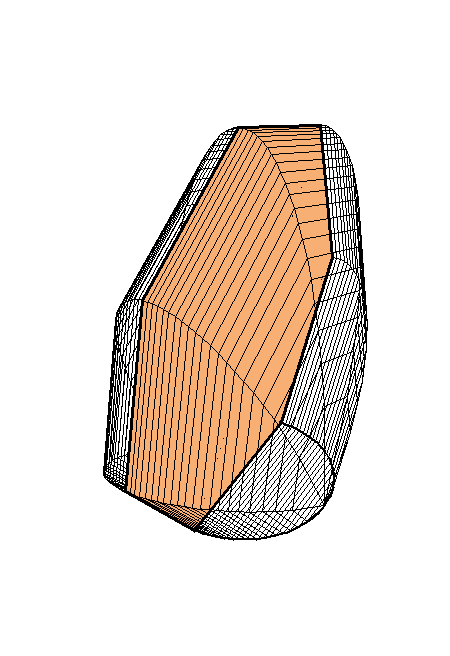
A cross-section is a regular heptagon.
Place the cursor over the image to start the animation.
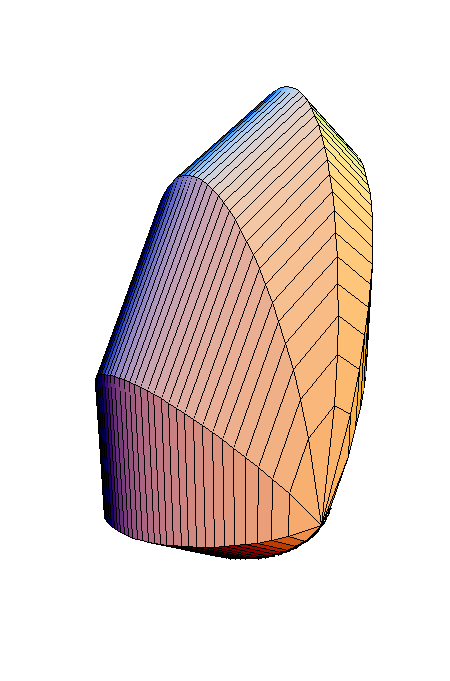
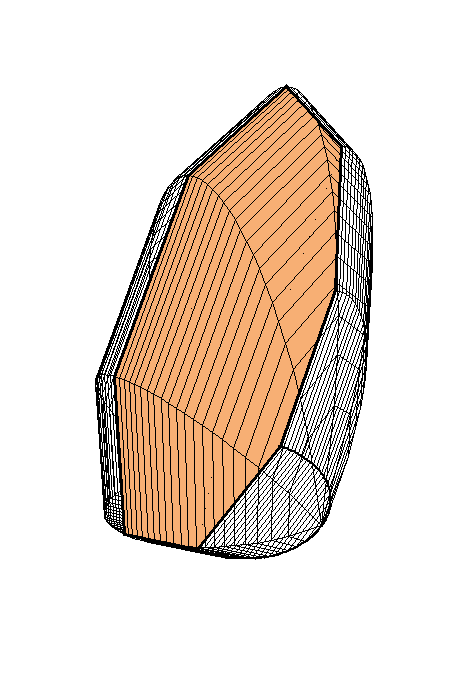
A cross-section is a regular octagon.
- Chapter 8
-
Below is an animation which shows a creation of a solid of revolution that we discussed in class today. For a different example Section 8.2. The second animation shows a disk sweeping the solid of revolution. That is how the volume of a solid of revolution is calculated.
Place the cursor over the image to start the animation.
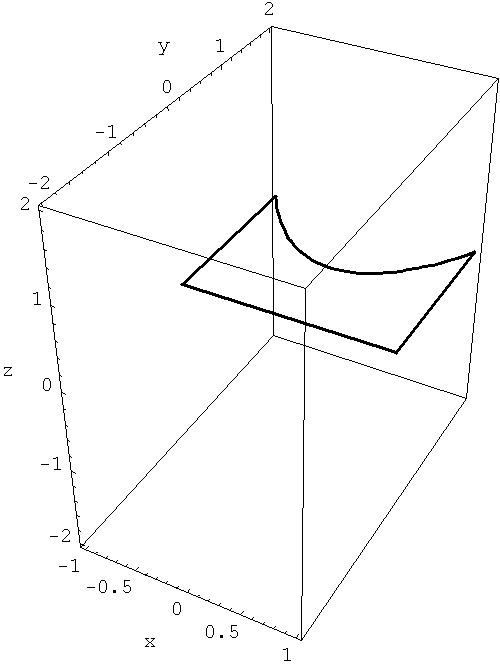
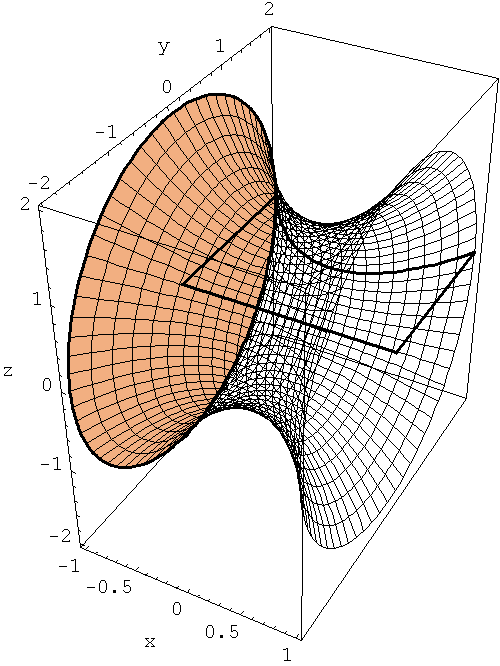
-
After I created one animation it is not a big problem to create others. So, here is another example. The function involved is
y = cos x.
Place the cursor over the image to start the animation.
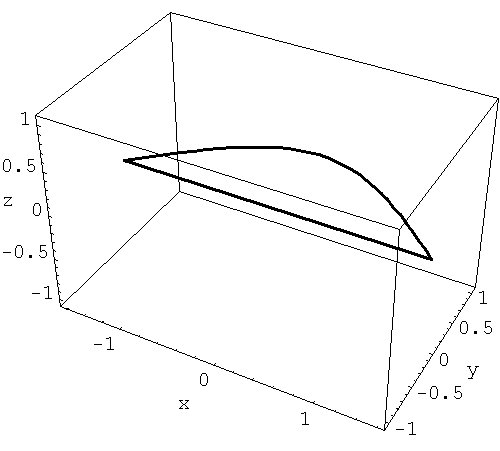
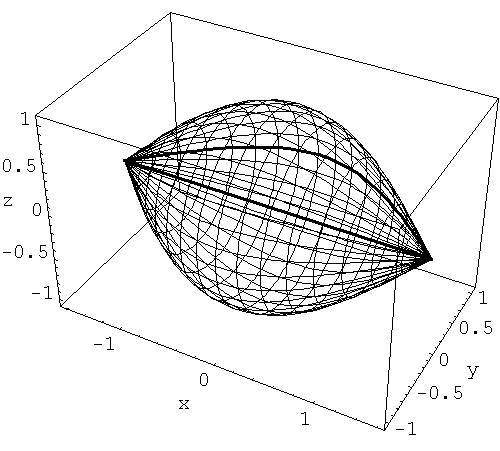
- As an exercise calculate the volumes of these solids of revolution.
- This is what I wrote during the exam.
- Here is a simplified Excel file for examples in Sections 7.5 and 7.6. It does not use macros.
- I was asked to comment on Problem 45, Section 7.4, in the textbook. Here is my solution without using trigonometric substitution.
- Here is a completely automated Excel file for examples in Sections 7.5 and 7.6. For this file to work on your computer you must allow Excel to use macros. The default setting in Excel is that the macros is disabled. If you have problems with this file stop by my office and we can solve them; I hope.
- Based on the simpler Excel files posted earlier (here and here) you might be able to write your own file that will cover examples from Sections 7.5 and 7.6.
- More integrals that we discussed in class are here.
- I am posting Austen's excellent solution of Problem 2 on Assignment 1.
- Some interesting integrals that we discussed in class are here.
- I am posting Lauren's impressive solutions for Assignment 1.
- Today's integral and a little more.
- This is what I wrote during the exam.
- Here is the histogram of grades on Exam 1.
- Here is Assignment 1 due on February 4, 2009.
- The first exam is next Tuesday. It will cover Chapters 5 and 6.
- Animations below are inspired by Section 6.5. In Section 6.5 we learned the formula for the position of a ball thrown vertically into the air. I added a vanishing trace to better convey a sense of motion.
- To make a more interesting animation I consider a baton thrown vertically into the air and which rotates about its center. For the center of the baton I use the equation of the position of the ball. Then, the endpoints of the rotating baton are determined using the parametric equation of a circle learned in Math 124 in Section 4.8. Again, I added a vanishing trace of the rotating baton to better convey a sense of motion. The trace consists of several (or rather many) previous positions of the baton which fade as the baton is getting further away.
Place the cursor over the image to start the animation.



- We are done with Chapter 6. There are several interesting problems in the Review Section. See for example 45, 46, 47, 59.
- The animation below is inspired by Section 6.5.
Place the cursor over the image to start the animation.

- Since we spent quite a bit of time discussing Maya's carpet "gone wild", here is a corresponding animation. The functions that I used in the animation are here.
Place the cursor over the image to start the animation.
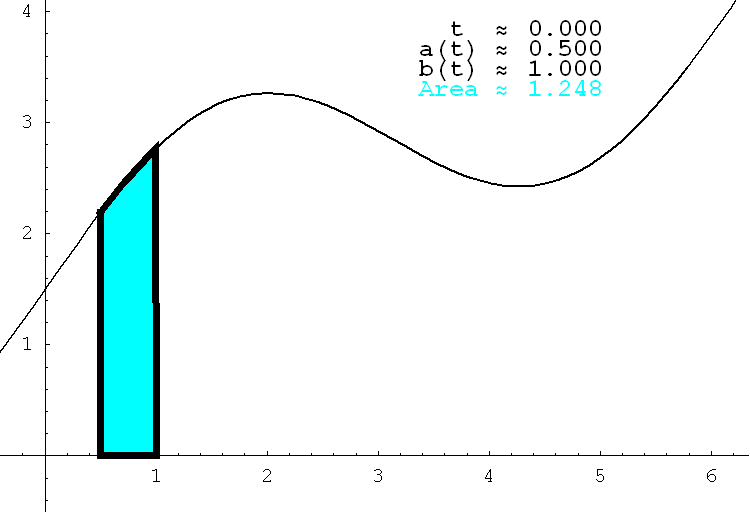
- The next animation illustrates how the functions a(t) and b(t) determine the changing interval of integration. In this animation the horizontal axes is t and the interval of integration is the vertical line segment.
Place the cursor over the image to start the animation.
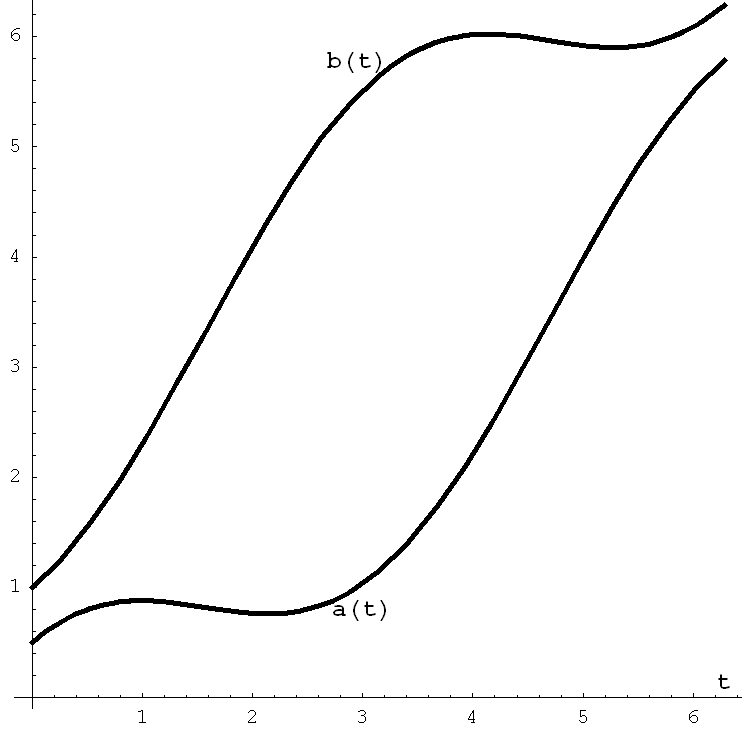
- Two problems and a formula related to Section 6.4.
- Today we introduced the concept of Maya's carpet. Notice that we skipped Section 6.3 and did 6.4 today. So, read and do the problems from 6.4. Also review earlier stuff.
- I posted an animation of Maya's carpet on Monday, January 12, 2009, but now I will move it here. Before that I present a simple animation of a function, its independent variable and its values. I need to choose colors. As before I am guided by mnemonic reasons. I could not find any color whose name starts with x. For example I looked at color names that can be used in HTML documents. Since we often use t to denote the independent variable, I decided to use teal for the independent variable. Since we use f for the function, the function values are in forest green.
- Now I will digress. If you decide to look for formulas for colors used in HTML documents, then you will find out that the decimal formula for teal is rgb(0,128,128). By the way, the formulas for red, green and blue are, respectively, rgb(255,0,0), rgb(0,255,0), rgb(0,0,255). Below we will use cyan for the area of Maya's carpet. The formula for cyan is rgb(0,255,255). In some sense teal is a half way from black, which is rgb(0,0,0), to cyan.
- Here is a function f in action.
Place the cursor over the image to start the animation.
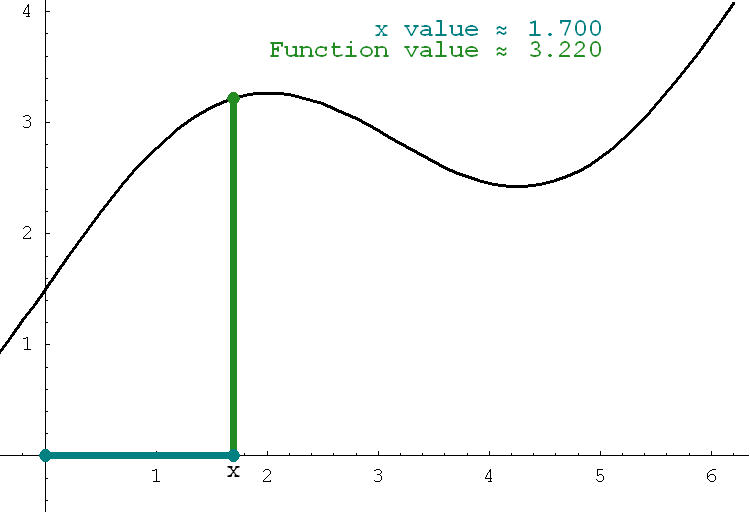
- Let f be a continuous function represented in the figure below by its graph, the black curve. Fix a number a and let x be an arbitrary number such that x > a. Then the cyan area in the animated figure below changes with x. In other words, the cyan area is a function of x. This function will be discussed in Section 6.2. In an old calculus book I saw that the cyan area was called Maya's carpet. I like this name since you can think of the animation below as a cyan carpet being unrolled in the xy-plane.
Place the cursor over the image to start the animation.
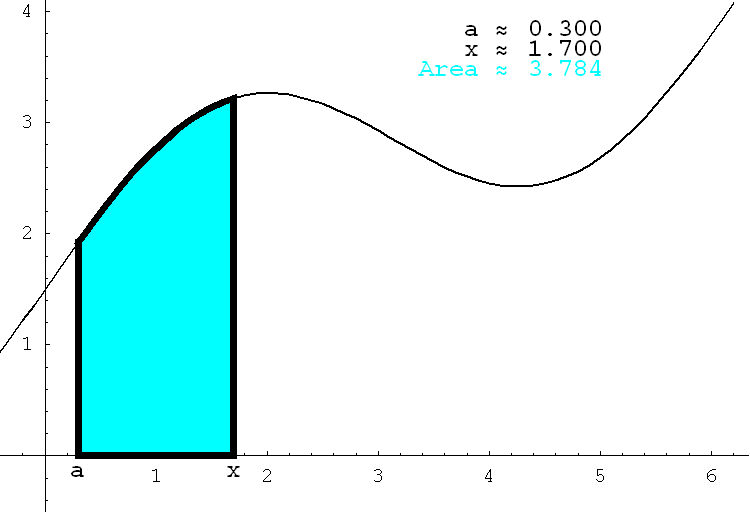
- Read and do problems from Section 6.1.
- Notice that Problem 47, page 277 in the Review of Chapter 5, is a very interesting problem. I did this problem in class today.
- Another interesting problem in the Review of Chapter 5 is Problem 24. In this problem you are asked to consider four integers n = 1, 2, 3, 4. But, you can consider more integers n = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, ... . Denote the corresponding definite integrals by I1, I2, I3, I4, I5, I6, I7, ... . Now arrange the numbers I1, I2, I3, I4, I5, I6, I7, ... from smallest to largest. Which properties from Section 5.4 are you using in your reasoning? Explain!
- This pdf file contains two interesting problems that can be solved by methods of Section 5.4. The first problem is similar to Problem 24 mentioned above.
- Suggested problems for Chapter 6 and an important table.
- Study and do problems from Section 5.4. Please also review the main points from the prior sections:
- the relationship of Riemann sums and definite integrals,
- the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus and how it is related to what you have learned in Math 124,
- the concept of the average value of a function.
- Below I give two illustrations, one from the past, one from the future. The first one, from the past, illustrates Riemann sums introduced in Sections 5.1 and 5.2. The second one, from the future, illustrates an important function which will be introduced in Section 6.4.
- This is a clickable illustration of Riemann sums. Riemann sums are in salmon color. The definite integral (that is the area under the function) is in Indian red.
I chose these colors for mnemonic reasons: Sum<-> Salmon, Integral <-> Indian.
At first I thought that these colors are not sufficiently different. But, afterwards I realized that the similarity of these colors might indicate that for a large n a Riemann sum is very close to the corresponding definite integral.
Click on the image to increase n.
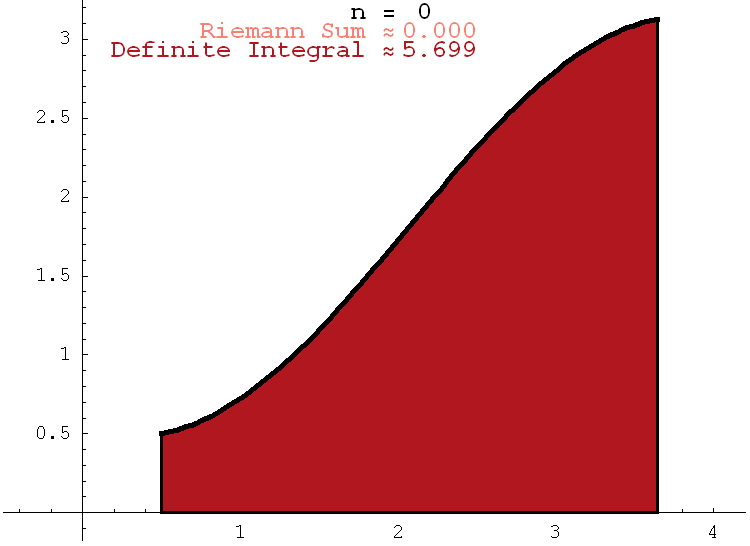
- Maya's carpet is moved to Friday, January 16, 2009.
-
Let a and b be real numbers such that a < b.
Let f be a positive function defined on the interval [a,b].
The average value of f over the interval [a,b] is the height of a rectangle whose base is (b-a) and whose area is the same as the area under the graph of f. - In the following four examples you can test your understanding of the concept of the average value of a function.
|
1.
|
2.
|
3.
|
4.
|
| Consider a unit square and all its chords which are parallel to one of its diagonals. | Consider a unit circle and all its horizontal chords. | Consider an equilateral triangle with sides of length 1 and all its horizontal chords. | Consider the segment of the parabola y=x2 between the points (-1,1) and (1,1) and all its horizontal chords. |
(Click on a figure to magnify.)
For each example answer the following question:
What is the average length of the chords?
- To answer this question for Example 4, you will need the result obtained in class using "integration by paper folding"; see January 6 below.
- Study and do problems for Sections 5.1, 5.2 and 5.3. Now, there are three main points here. First, understand the relationship of Riemann sums and definite integrals. Second, understand the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus and how it is related to what you have learned in Math 124. Third, understand the concept of the average value of a function.
- Finally, here is a completely automated Excel file in which you can chose the function, the interval of integration and the number n. Choosing a function is a little tricky, but it might be worth learning, since Excel is an omnipresent, useful tool. For this file to work on your computer you must allow Excel to use macros. The default setting in Excel is that the macros is disabled.
- Study and do problems for Sections 5.1, 5.2 and 5.3. There are two main points here. First, understand the relationship of Riemann sums and definite integrals. Second, understand the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus and how it is related to what you have learned in Math 124.
- It might be easier to do numerical problems in Excel. Excel is available on all computers on campus. If you do not have your own copy of Excel you can use a free alternative: OpenOffice.
- To use the Excel files in the items below, click on the underlined word "Here"; in a pop-up menu that appears, your browser will offer you to save the file in your directory. After saving the file you can open it with Excel.
- Here is a sample Excel file for Example 1, with n=10, in Section 5.2 (page 249).
- Here is the same example with n=250.
- Here is a somewhat automated Excel file in which you can chose the interval of integration and the number n.
- Notice that Problem 34 in Section 5.2 is closely related to Example 1 in Section 5.2. I briefly mentioned this in class today.
- Create your own Excel files for other functions.
- Please read the information sheet. It contains some important information.
For example, the in-class exams will be on
Tuesday, January 27, Tuesday, February 17, and Friday, March 6.
The final exam is comprehensive. It is scheduled for
Tuesday, March 17 from 8:00 to 11:00. Notice: the final is scheduled for three hours.
- The information sheet
- Chapter 5
- A proof that cos(pi/5) is exactly one half of the golden ratio.
- To do integration by paper folding you will need three copies of the handouts bellow.
Print this handout on heavy yellow paper. Print this handout on a transparency.